What is an IP Address and Types of IP Address ?

What Is an IP Address?
IP address stands for internet protocol address; it is an identifying number that is associated with a specific computer or computer network. When connected to the internet, the IP address allows the computers to send and receive information.
Types of an IP Address :
1.Public IP Address
2.Private IP Address
3.Static IP Address
4.Dynamic IP Address
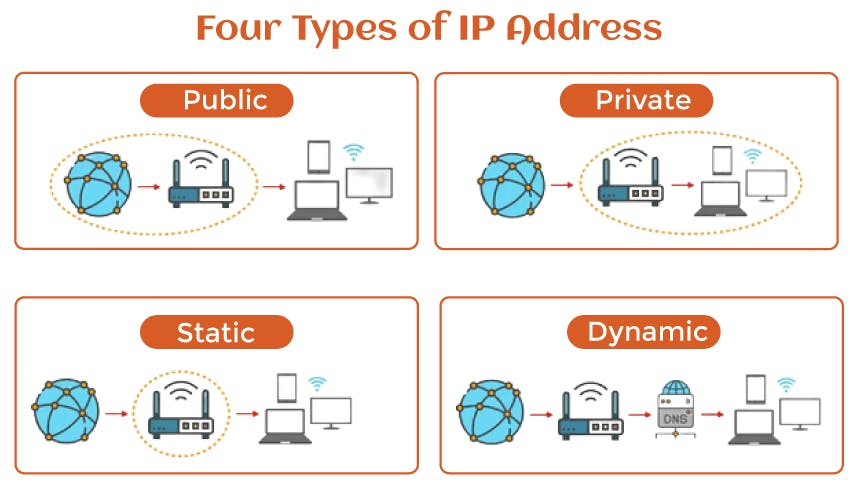
1.Public IP Address :
A public Internet Protocol address is an Internet Protocol address accessed over the Internet. Like the postal address used to deliver mail to your home, the public Internet Protocol address is a different international Internet Protocol address assigned to a computer device. The web server, email server, and any server device that has direct access to the Internet are those who will enter the public Internet Protocol address. Internet Address Protocol is unique worldwide and is only supplied with a unique device.
2.Private IP Address :
Everything that connects to your Internet network has a private IP address. This includes computers, smartphones, and tablets but also any Bluetooth-enabled devices such as speakers, printers, or smart TVs. With the growing internet of things, the number of private IP addresses you have at home is likely to increase.
3.Static IP Address :
A static IP address is a fixed address assigned to a device that remains constant. They are typically used for hosting websites or running servers. By having a fixed IP address, users can easily connect domain names to their servers, ensuring that their websites or services are always accessible.
4.Dynamic IP Address :
A dynamic IP address refers to an address assigned to a device temporarily by an ISP. Dynamic IP addresses are typically assigned to devices such as computers, smartphones, or routers. They provide a level of anonymity and security as the IP address changes periodically, making it more difficult to track a specific device or user.
How are IP Addresses Generated?
IP addresses are generated automatically using an integrated algorithm by the Internet Of Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). IANA then allocates IP address blocks toes regional internet registries (RIRs) who in turn geographically distribute these blocks to internet service providers (ISPs). To generate individual IP addresses for their customers, ISPs typically use a technique called Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). DHCP allows devices to have an IP address assigned automatically when they connect to a network.
At a more technical level, IP addresses are generated using two main versions of Internet Protocol (IP): IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 addresses are 32-bit numbers, represented in a dotted-decimal format (e.g., 192.168.0.1), while IPv6 addresses are 128-bit numbers, represented in a hexadecimal format (e.9., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334). By following the rules and protocols outlined by IANA, RIRs, and ISPs, devices can obtain unique identifiers for communicating online.
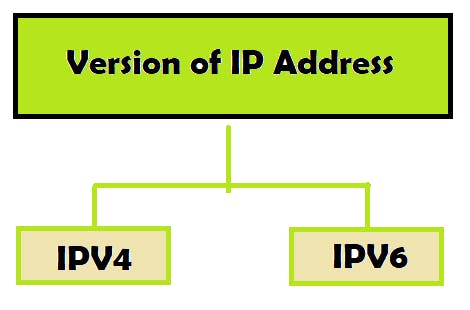
Version of IP address:
Currently there are 2 versions of IP addresses are in use i.e IPV4 and IPV6.
IPV4 (Internet Protocol Version 4): It is the first version of Internet Protocol address. The address size of IPV4 is 32 bit number. In this Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) with respect to network security is optional. It is having 4,294,967,296 number of address still we are seeing a shortage in network addresses as the use of network & virtual devices are increasing rapidly.
IPV6 (Internet Protocol Version 6): It is the recent version of Internet Protocol address. The address size of IPV6 is 128 bit number. In this Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) with respect to network security is mandatory. It allows 3.4 x 10^38 unique IP addresses which seems to be more than sufficient to support trillions of internet devices present now or coming in future.
