Table of contents
- What is Traceroute Command ?
- A traceroute provides a map of how data on the internet travels from its source to its destination. When you connect with a website, the data you get must travel across multiple devices and networks along the way, particularly routers.
- A traceroute plays a different role than other diagnostic tools, such as packet capture, which analyzes data. Traceroute differs in that it examines how the data moves through the internet. Similarly, you can use Domain Name System time to live (DNS TTL) for tracerouting, but DNS TTL addresses the time needed to cache a query and does not follow the data path between routers.
- What is Traceroute Used For?
- How To Run a Traceroute, Explained
- To run traceroute on a Mac or Linux system, do the following:
- Open up an instance of Terminal.
- Type in the phrase “traceroute [hostname]” and press enter.
- On a Windows system, you can:
- Go to the Start menu.
- Select Run.
- Type in “cmd” and then hit “OK.” This initiates a command prompt.
- Type in “tracert [hostname]” and press enter.
- The term “hostname” or host is the website you are interested in or the IP address of a server, router, or device. The traceroute reports on this destination point. After the traceroute is done, it terminates on its own.
What is Traceroute Command ?
A traceroute provides a map of how data on the internet travels from its source to its destination. When you connect with a website, the data you get must travel across multiple devices and networks along the way, particularly routers.
A traceroute plays a different role than other diagnostic tools, such as packet capture, which analyzes data. Traceroute differs in that it examines how the data moves through the internet. Similarly, you can use Domain Name System time to live (DNS TTL) for tracerouting, but DNS TTL addresses the time needed to cache a query and does not follow the data path between routers.
What is Traceroute Used For?
An Internet Protocol (IP) tracer is helpful for figuring out the routing hops data has to go through, as well as response delays as it travels across nodes, which are what send the data toward its destination. Traceroute also enables you to locate where the data was unable to be sent along, known as points of failure. You can also perform a visual traceroute to get a visual representation of each hop.
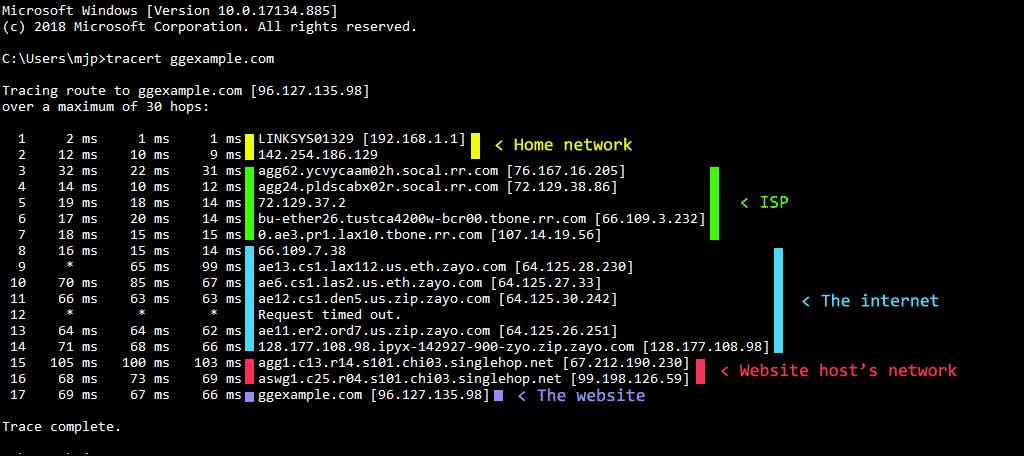
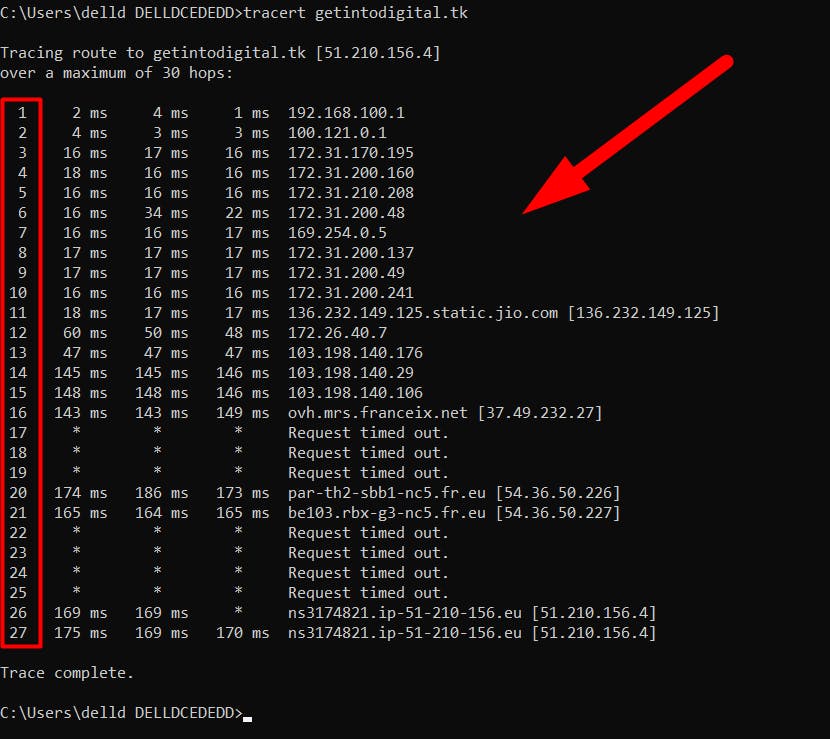
How To Run a Traceroute, Explained
To run traceroute on a Mac or Linux system, do the following:
Open up an instance of Terminal.
Type in the phrase “traceroute [hostname]” and press enter.
On a Windows system, you can:
Go to the Start menu.
Select Run.
Type in “cmd” and then hit “OK.” This initiates a command prompt.
Type in “tracert [hostname]” and press enter.
The term “hostname” or host is the website you are interested in or the IP address of a server, router, or device. The traceroute reports on this destination point. After the traceroute is done, it terminates on its own.
What is Ethical Hacking and Types of Hackers ?